Introduction to Portal Hypertension
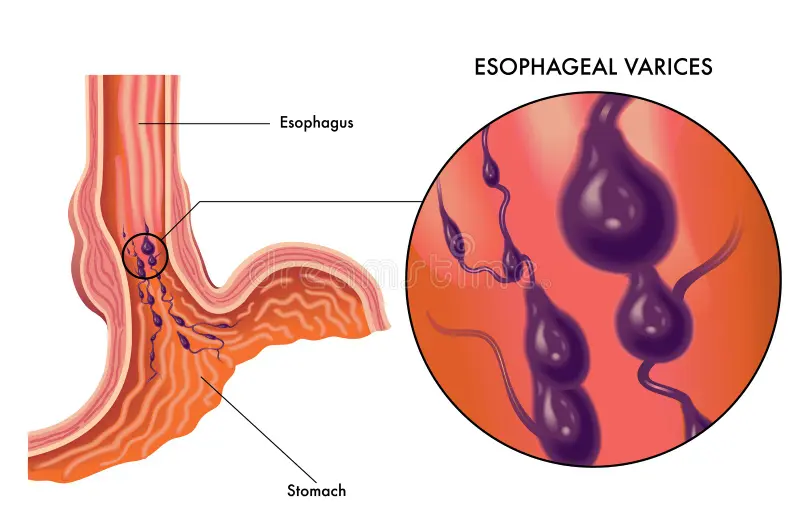
Portal hypertension is a health issue characterized by a rise in blood pressure within the portal venous system that conveys blood from the digestive organs to the liver. This increased pressure usually results from obstacles or impediments to blood flow within the portal vein and its branches.
One of the commonest causes of portal hypertension is cirrhoses of the liver which cause structural changes in liver tissue, thus impairing blood flow. Consequently, blood is shunted into smaller veins causing them to dilate and get filled up with blood.
This could lead to severe complications such as variceal bleeding, ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdomen), hepatic encephalopathy (brain dysfunction due to failure of the liver) and splenomegaly (enlarged spleen).


